Table of Contents
The rise of anatomy as an accepted science and the dissection of human cadavers propelled medical knowledge forward beginning in the 17th century and throughout the 19th century. During that time medical schools began requiring dissection as an essential part of a young doctor’s education. But, this created a conundrum. How to acquire the necessary dead bodies? Colleges legally acquired the remains of executed criminals, but society generally frowned upon the dissection of human remains. In fact, the dismemberment of the body for medical study was viewed as an abomination, in direct conflict with the religious ideology of Victorian America. In their view, the desecration of the body resulted in the release of the soul, preventing the individual from rising from the grave at the time of the Resurrection.

With few other options, body snatching became endemic to impoverished areas surrounding major medical institutions. During these years, public discontent with the practice of stealing bodies from cemeteries often turned violent. In the earliest and most chilling example, on April 16th, 1788 a riot broke out in New York City after a medical student jokingly waved the arm of a cadaver at a group of children playing nearby. A boy in the group had watched his mother die shortly before this incident, and the medical student told the child that the body belonged to his mother. In outrage, a mob gathered and broke into the hospital. They found bodies in multiple stages of dissection. As a result, physicians in the city were forced into hiding for their own safety.
In the decades that followed, there were plenty of bodies available and ready for the taking for the University of Maryland located in Baltimore. A thriving port city, Baltimore was in a period of rapid growth and the city’s meager infrastructure could not keep up. An antiquated sewage system in the city quickly led to a public health nightmare. Outbreaks of cholera, yellow fever, and dysentery led to an abundance of fresh bodies. Cemeteries of poor whites and free blacks were targeted most frequently. Their inability to afford medical care led to regular burials in the city’s graveyards. The impoverished were often placed in pine coffins, a cheap soft wood that was easy to break open. Baltimore, a city with a long history of mob violence protests, suffered its first riot as a result of body snatching in 1807. Protests became so common that the University of Maryland had secret passageways under the building to allow students and faculty to escape their angry neighbors.
In the 1820s, the school had no problems keeping up with their own demand for corpses once they hired a man named Frank. Officially he was listed as the building’s janitor, but he supplied the corpses for a growing medical school. Frank’s last name is lost to history; the university remained cautious and only referred to him by his first name. Frank excelled at his job and the faculty quickly found itself with an overabundance of specimens. With the surplus supply, professors found an opportunity to increase the school’s bottom line. They began shipping surplus bodies to colleges and universities that lacked a prodigious body snatcher such as Frank. In a letter to a colleague in Maine, a professor in Baltimore boasted of Frank’s success, assuring his counterpart that “a better man never lifted a spade.” He described the pricing for three bodies stored in whiskey: a reasonable $50. The barrels themselves cost $1. The university charged an additional 35 cents per gallon of whiskey. And, the value of a dead loved one plucked from their eternal rest in a Baltimore graveyard? Just $10 each.
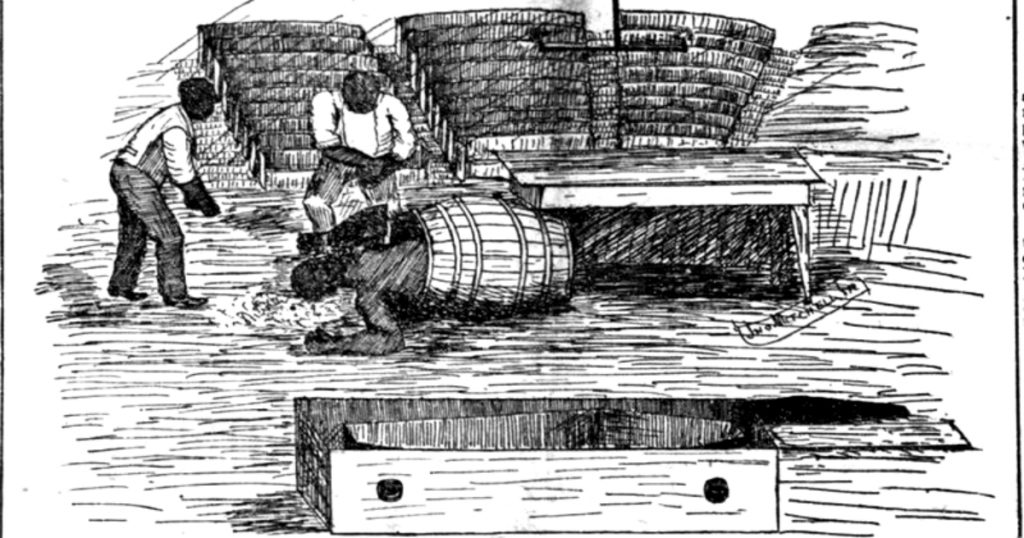
But, one might ask, what happened to the left-over whiskey? There are rumors. Stories that bring a shudder. Surviving accounts claim the poor students imbibed it, eager to get their liquor no matter how questionable the source. Others claim that faculty in medical institutions may have decided to recoup some of their losses and sold the liquor to their communities’ more questionable establishments, and creating the term “rot-gut whiskey.”
Frank and the University of Maryland were part of a larger history of body snatching and the evolution of modern medical education. Digging into the history of medical universities in America and Europe provides a horrifying glimpse into the shadowy corners of early academia. A world not only where bodies to be dissected were shipped in barrels of whiskey, but where bones were tossed into the basement of the Georgia Medical College and an Edinburgh doctor refused to accept that his specimens were supplied by serial killers. An immoral treatment of the dead with the hope of saving the living.
Learn more on this subject with Education Coordinator John Lustrea
About the Author
Katie Reichard is the Reservation Coordinator for the National Museum of Civil War Medicine. She, arguably, has the best dog in the world.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.